The generative AI tool ChatGPT creates novel content by responding to user prompts and may become increasingly powerful and accessible. However, ChatGPT use has some challenges and ethical issues attached. To help small businesses become better equipped at using such tech, we surveyed 463 generative AI users to learn about its various benefits and limitations.
In this article
Generative artificial intelligence (AI) tools continue to appear in headlines across industries. The technology is anticipated to revolutionise the way we work by potentially increasing productivity and performance. Open AI’s ChatGPT was the generative AI forerunner platform that captured the world’s attention. Through its ability to understand and respond to natural language requests, ChatGPT only took five days to attract a million users.
We learnt from part one of this two-part series that two-thirds of respondents frequently use generative AI tools at work. Following the rapid uptake of the technology, risks such as privacy and data protection may have been questioned in the aftermath of the hype. Keeping this in mind, how aware are organisations of the technology's capabilities or limitations in the workplace?
GetApp surveyed 463 generative AI users to learn more about the use of tools such as ChatGPT, their concerns about such usage, and the benefits they get from it at work. The study zooms in on ChatGPT usage before finally evaluating the concerns of utilising generative AI as a whole. The full methodology can be found at the end of this article.
75% of respondents use ChatGPT
The popularity of ChatGPT is evident among Australian employees, where three-quarters of respondents said they use ChatGPT, followed by 18% who use DeepMind’s Alpha Code. Due to the rapid uptake of ChatGPT, it's no surprise that many use this generative AI tool, but why does it attract so much attention?
ChatGPT can be used in many different ways, thus appealing to various employees working in different sectors. This generative AI tool can explain concepts, solve problems, produce new creative ideas, translate content, create unique images, write and respond to emails, and so on. Moreover, the tool can either be used as an aid or even be prompted to produce stand-alone work.
What is the meaning of ‘GPT’ in ‘ChatGPT’?
OpenAI’s ChatGPT tool is based on the generative pre-trained transformer model known as ‘GPT’ which is trained on a massive amount of text data. The technology has been taught to simulate human-like conversations, to ‘chat’ and provide informed answers to queries or prompts based on its extensive pre-input knowledge and skills. ChatGPT uses natural language processing (NLP), a model which enables comprehension and generation of human language. NLP uses neural networks and complex algorithms known as deep learning to function.
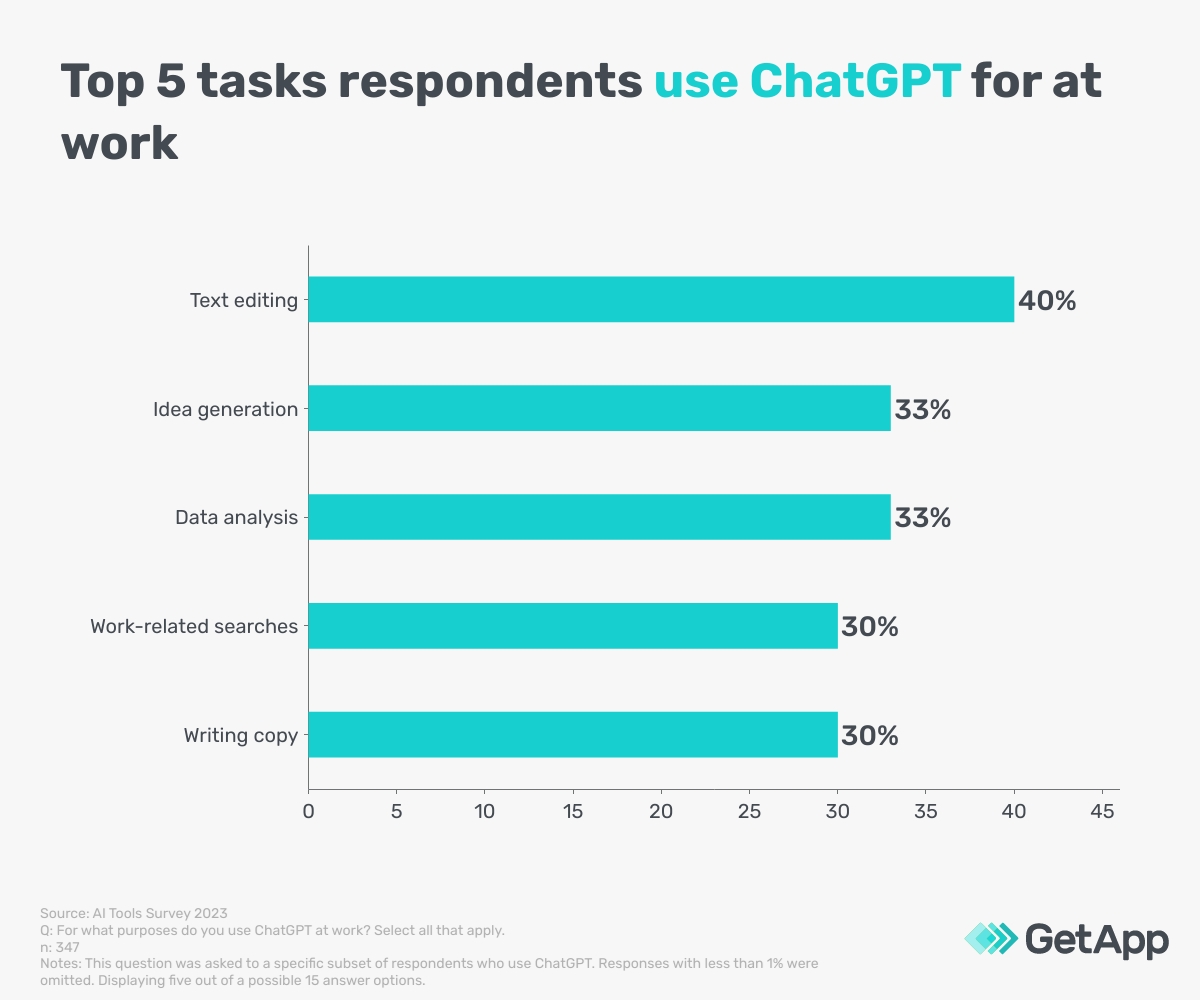
In addition to ChatGPT's popularity, our survey found that its users frequently use the tool. Of those that use ChatGPT, about a third (34%) use the tool a few times per week, and a further 30% use it between three and 10 times per day. Such frequent use may suggest that users are content with ChatGPT outputs. Although text editing was the most frequently cited (40%) purpose for its use, it also fulfils various other purposes at work, as indicated by users in the graph below.
While NLP enables ChatGPT to be more user-friendly and accessible to millions of users with its ability to solve a wide range of problems, the success of its output is dependent on how well the tool is prompted.
How to prompt ChatGPT effectively
ChatGPT users are able to have a conversation with the software and direct it to generate successful results. Companies can educate their employees on how to successfully and safely prompt ChatGPT to generate desired outcomes. Here are a few ways users can more effectively get going with the software:
- Be specific: Clearly outline the information you’re seeking or the task you want ChatGPT to perform. Being specific reduces ambiguity and helps the platform understand your requirements.
- Provide context: Including relevant background information and context in your prompt allows ChatGPT to better understand the scope and purpose of your request. For example, prompting ChatGPT to write an article may involve indicating the target audience and a specific structure.
- Refine your prompts: If the initial response is not quite what you're looking for, refine the initial prompt. Add more detail, rephrase the prompt, or clarify the context to align the output with your expectations. For example, you may want to refine the context from the above example to include a target audience with no prior knowledge of the topic.
- Ask for advice: Ensure your prompt is as thorough as possible by asking ChatGPT what other details it needs from you to produce the best output.
ChatGPT is the most popular generative AI tool with the majority of respondents, however, how much of its popularity is driven by effective results? We explore that in the next section.
98% of ChatGPT users say it is effective
An overwhelming combined total of 98% of ChatGPT users rated the technology as effective, of which 37% said the results were ‘highly effective’ based on their experience of using it at work. The scope of ChatGPT’s use is varied and despite most respondents using it for text editing, it is largely regarded as effective for various use cases. In addition, ChatGPT users cite the following as the main benefits of applying the technology at work.
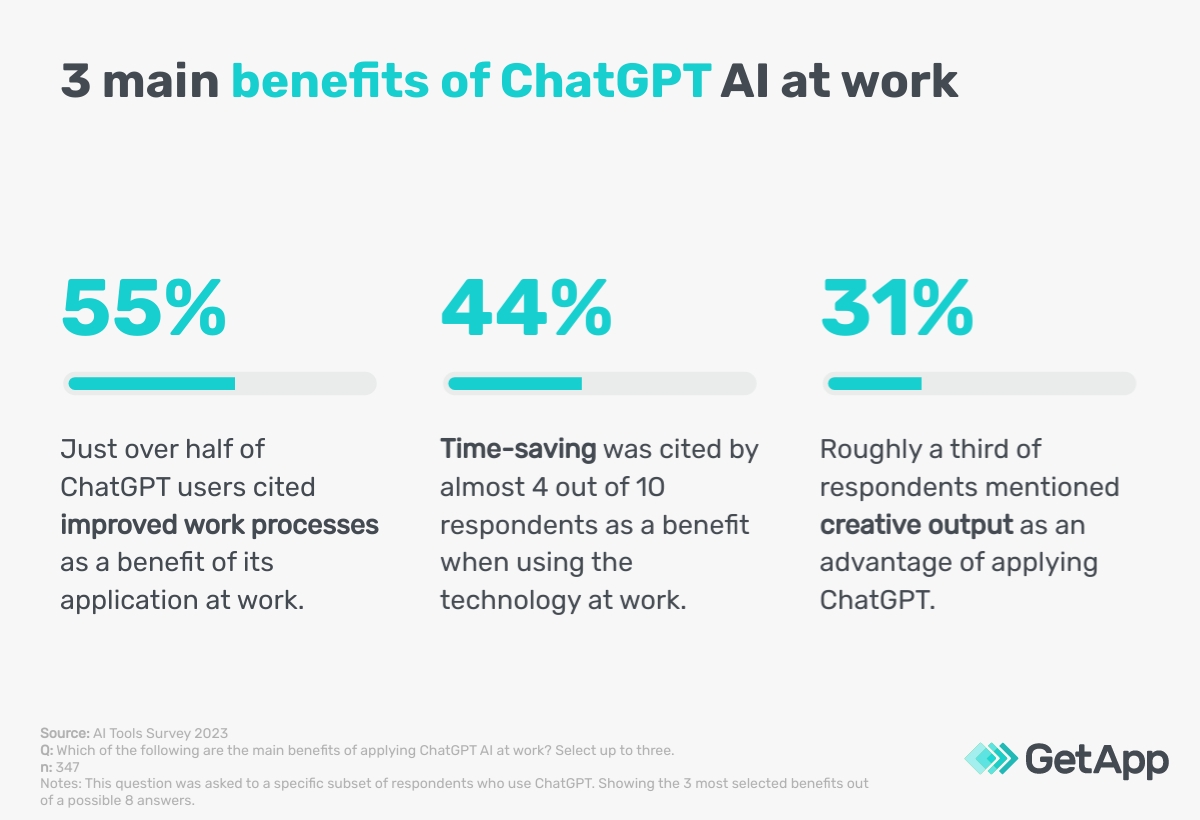
On the contrary, only 10% of ChatGPT users cited enhanced security and safety monitoring as a benefit. Despite ChatGPT being cited as effective, this result may imply that users have either not received proper training on how to use the technology for safety and security or they just may just not use ChatGPT for this purpose. To find out more about the limitations of ChatGPT, we asked users about their concerns and cover these in the next sections.
Use of ChatGPT requires error verification
Although ChatGPT offers many benefits, it must be used with caution. Especially as there may be a temptation to use its outputs as stand-alone work due to its ability to write texts in a human-like manner. In fact, over half (55%) of ChatGPT users agree to some extent that ChatGPT content can rival human creations, and a further 34% say it definitely can.
However, ChatGPT users must be wary of the dangers of text outputs containing information from an unverified source that may be outdated, biased, or infringes copyright material. As such, a plagiarism checker tool can help check the veracity of the content generated using tools such as ChatGPT. Users must also ensure they fully understand the limitations of the unpaid version of ChatGPT as it may not use up-to-date information.
There may also be concerns over too much reliance on such tools. Our survey found that 41% of ChatGPT users expressed concerns that they may develop an over-reliance on it and other AI tools to perform tasks, while 31% cited the spread of inaccurate information due to users considering ChatGPT’s response as definitive. In relation to the latter concern, a combined total of 89% of ChatGPT users verify the outcomes of ChatGPT for errors or inconsistencies, of which 42% meticulously review and verify every response before using it.
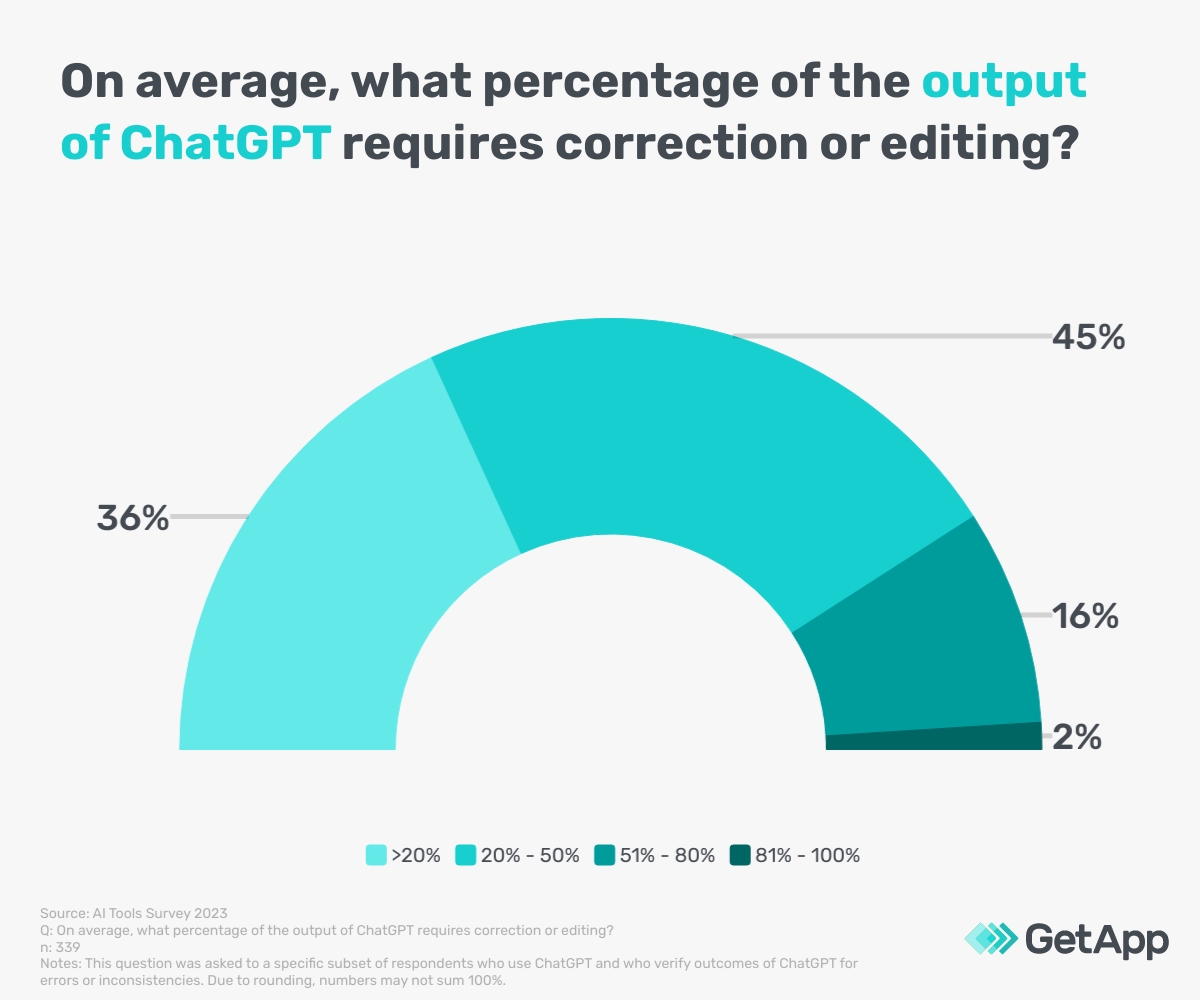
Despite a need for verifying ChatGPT’s outputs, users make use of ChatGPT frequently and fear becoming reliant on the technology.
How to verify AI-generated content
It may be vital to verify AI-generated content to ensure accuracy and reliability. Here are a few steps users can take to verify such content:
- Justify claims: Examine the claims made within AI-generated content and check for bias. Look for evidence from credible sources to support such claims and ensure that the content aligns with other reliable information available.
- Ensure credibility: Check the credibility of the source of where the AI-generated content originates. Verify information sources with SEO tools to prove their domain authority and trustworthiness.
- Assess plausibility: Look for logical inconsistencies, contradictions, and analyse the content for coherence and consistency.
- Check for plagiarism: A plagiarism checker can detect content similarities within written documents and websites to check for copied/duplicate content.
41% of respondents are concerned about job loss due to generative AI
As a result of the evolution of generative AI, respondents from our survey are aware of a possible job transformation, and a third (33%) are somewhat concerned, while 8% are very concerned about losing their jobs due to generative AI. However, a recent collaboration report between Microsoft and the Tech Council of Australia found that generative AI could benefit the national economy and increase jobs through the creation of new products and services and improve efficiency levels in existing industries.
About a third (32%) of respondents perceive that 11%-20% of their job can be replaced by generative AI output. As such, 36% of respondents say they have more time to focus on higher-value tasks as a result of job transformation brought about by generative AI. From these stats, we can deduce that although there is a concern about job loss among Australian employees, generative AI technology presents an opportunity to be more efficient at work by giving employees more time to work on intricate tasks.
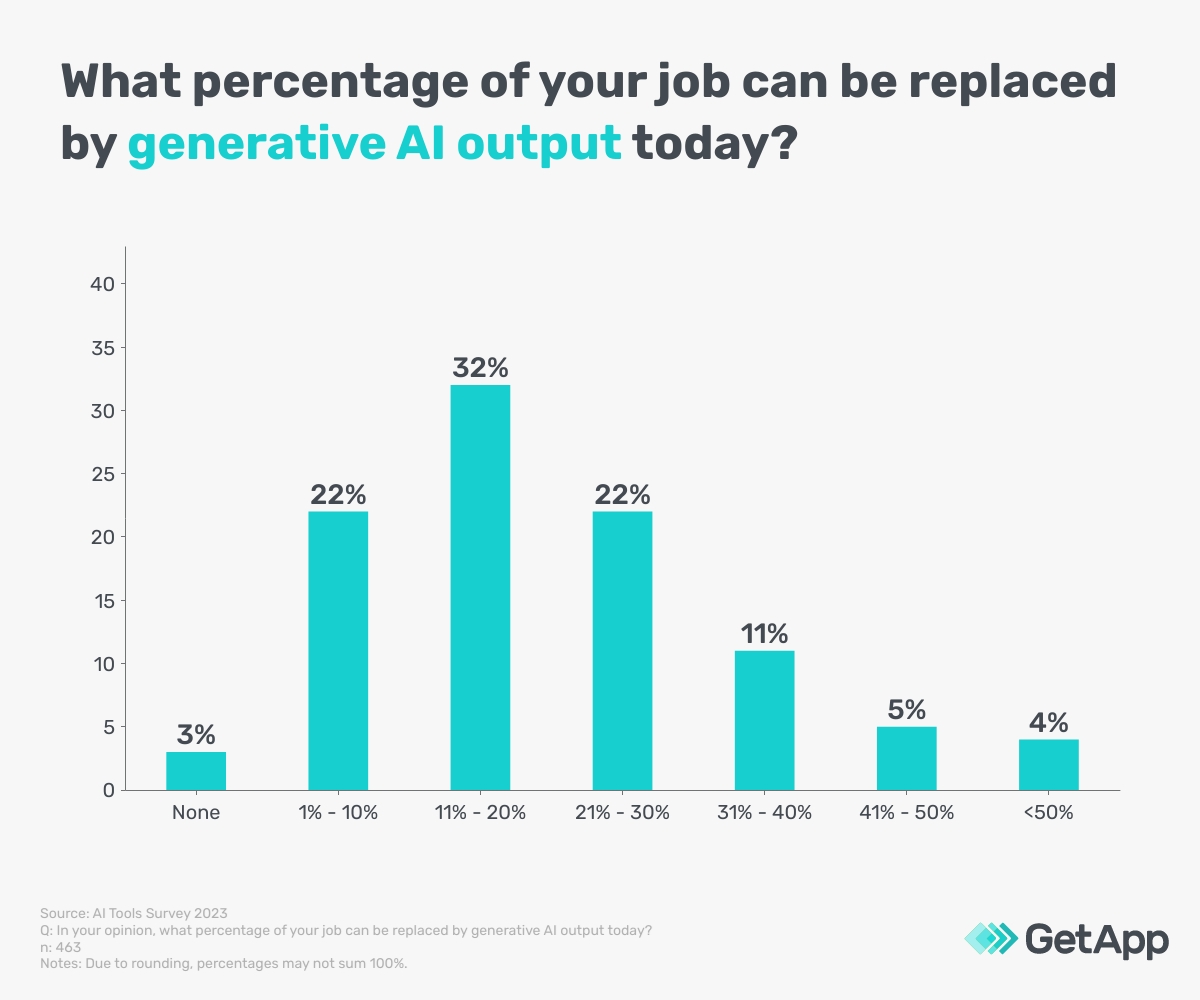
Organisations looking to adopt generative AI technology should communicate the possibilities that it presents to employees rather than have their employees fear potential job loss or replacement as a result of adopting it. But the possibilities depend on the technology's responsible uptake, regulatory clarity, and upskilling of the technology. We discover what risks and concerns companies must know before implementing generative AI tools in the next section.
Companies must get acquainted with generative AI risks
The uptake of generative AI tools —such as ChatGPT— may have become widely popular, but its adoption by businesses comes with a degree of ethical risk. Notably, 45% of respondents cited privacy and data security as their main ethical concerns, followed by misuse of AI-generated content (30%). Furthermore, respondents foresee companies exposing themselves to cybersecurity and regulatory compliance risks using generative AI at 51% and 41%, respectively.

From the results of this study and following the rapid uptake of generative AI technology, a combined total of almost 9 out of 10 users verify ChatGPT outputs despite citing that generative AI tools such as ChatGPT are indeed effective. Understanding the risks and limitations of generative AI can help organisations become more familiar with the technology and adapt its use for more efficient outputs and workflows. When starting out with generative AI tools, companies should consider the following aspects:
- Transparency: Be open about the use of generative AI tools and clearly communicate the abilities and limitations of the technology to your teams. Reporting the use and results of the technology in a simple and transparent way can also substantiate any claims about its abilities.
- Trustworthiness: Test the results of generative AI extensively internally with stakeholders and evaluate employee use cases. Determine how trustworthy the technology is before using it to create content available to the public.
- Security: Ensure that there are appropriate measures for privacy protection. Establish security protocols that can track biases by continually validating outputs.
Methodology
To collect this data, GetApp interviewed 463 Australian employees online in June 2023. The candidates had to fulfill the following criteria:
- Australian resident
- Between the ages of 18 and 65
- Employed full or part-time
- Uses a computer/laptop to perform daily tasks at work
- Uses generative AI tools for their work at least a few times per month
- Must have understood the definition of generative AI
Respondents were provided with the following definition:
'Generative AI (GAI) refers to a type of artificial intelligence that is capable of generating new, original content such as images, videos, music, code, or text. It typically uses deep learning techniques and neural networks to analyse and learn from large datasets and uses this information to generate content that resembles human creations. Some examples of generative AI tools are ChatGPT, Bard, and DALL-E.'
